This photograph shows the High School Officer Training Corps in 1915. I have previously written about what happened to the teachers in the years after this iconic photograph was taken.
This time I want to write about the fates of some of the boys. You might be forgiven for thinking that these twelve individuals are all far too young to have left the school, joined the army, trained as officers, gone to the Western Front and then been killed. But you would be wrong. Three of these young men were to perish. And this, tragically, is a much better casualty rate than the rugby team of Boxing Day, 1913. On the other hand, though, it is still a staggering 25%!
On the back row of the photograph are, left to right, F.A.Bird, J.R.Coleman, D.J.Clarkson, J.Marriott, A.W.Barton, G.R.Ballamy, S.I.Wallis and W.D.Willatt.
On the front row are, left to right, L.W.Foster, V.G.Darrington, Second Lieutenant J.L.Kennard, Captain G.F.Hood, Second Lieutenant L.R.Strangeways, G.James and R.I.Mozley.
I have not been able to find information on all of the boys in this photograph, but here is what I have come up with:
In January 1918, the school magazine, “The Highvite” carried a list of the school prefects, with their nicknames. They included the Captain of the School, F.A.Bird (Dicky) and A.W.Barton (Fuzzy). Both of them feature in the photograph.
They seem to have been very good friends and we have already noted their advertisement “for poisons, the quality of which was endorsed by Mr.Strangeways”. I know nothing further of Mr Bird except that his first name was Francis and he was the best friend of Harold Arno Connop, a Flight Sub-Lieutenant in the Royal Naval Air Service, who was killed at Dunkirk on Sunday, March 31st 1918:
Arthur Willoughby, “Fuzzy”, Barton had an unbelievably varied life. In his last year at the High School, he was Captain of the School and during the First World War, he became a Second Lieutenant in the Royal Engineers Signal Service, until he was demobilised in December 1918.
Arthur then went to Cambridge University to study Physics and helped Lord Rutherford to split the atom. He became a top flight football referee and officiated in the only football match that Adolf Hitler ever watched. I will be telling you his story in another blogpost (Fuzzy Barton, not Adolf Hitler).
Arthur had been, however, the recipient of a gangster type extortion racket in the early part of his school career. The Prefects’ Book records that on Tuesday, October 27th 1908:
“…A meeting was held at 2.30 p.m. in the Library. All the prefects were present. M.M.Lyon was reported for bullying A.W.Barton during the preceding day. He had tried to make Barton accompany him home & as Barton refused, he dragged him along Forest Road towards Waverley St. Lyon also hit Barton with the knob of his umbrella on his head just behind the ear. This blow had raised a big lump on Barton’s head. Lyon only allowed Barton to go home on receiving a promise that he would bring him a penny in the afternoon. As Barton did not bring the money, Lyon thrashed him again in the afternoon.
Lyon admitted the offence, & was treated as a first offender & received 6 strokes.
On the next day, however, Mr Woodward told the school captain that Lyon had treated other boys in a similar way, & had obtained 2d, from J.B.Cooper. Dr.Turpin stated that he had warned Lyon previously, & threatened him with expulsion on a repetition of the offence. Mr Dark had also complained about Lyon’s bullying propensities. H.J.Hoyte reported Lyon at the end of the summer term for swearing, but Lyon had not been punished as he was away from School. Taking all this into consideration, the prefects offered Lyon the alternative of 15 strokes or expulsion by the Doctor. Lyon chose the strokes.”
Richard Inger Mozley was born on May 10th 1898, the son of Albert Henry and Laura Mozley. He entered the High School on January 14th 1908, at the age of nine.
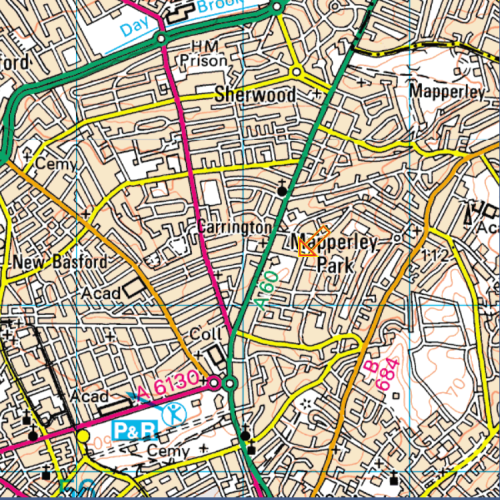
In the School Register his address is given as Grosvenor Avenue, Mapperley Park (1908), and then later, “Hollies”, Burton Joyce, Nottingham. One other website gives the family address as 17a, Woodborough Road, Nottingham. His father, Albert Mozley, was a Coal Merchant.
Richard was a Sergeant in the O.T.C. and, as such, was recommended for a commission in the Army both by Captain Hood and by the Headmaster, Dr G.S.Turpin. Richard had already applied himself to the O.T.C. of the 3rd Battalion of the Sherwood Foresters, but they were already vastly oversubscribed, and he duly joined the 3rd York & Lancaster Regiment.
He was then attached to the 36th Battalion of the Machine Gun Corps (Infantry):
During the course of “Operation Michael”, the Germans’ last do-or-die effort to win the war before the Americans began to influence the outcome of the conflict, Richard’s unit was assigned to defend the Forward Zone. Richard himself was stationed in the forward trenches, but he and his colleagues were quickly overwhelmed by the sheer weight of numbers of the enemy. They perished more or less to a man.
Richard was listed as missing, presumed killed, on March 21st 1918. At the time he was nineteen years of age:
By the time he died, he was living in Hoveringham and his parents remained at the “Hollies”, Burton Joyce. In due course, a letter arrived from Sergeant Crenston:
“When Lt. Mozley came back to the Coy. in Dec. last, he took charge of “A” Section and I being the section Sgt. was nearly always with Mr. Mozley and when in the line that terrible morning 21st March Mr. Mozley, myself and about 19 others were in the same position and dugout, the most forward position of the Division, 4 guns with us; at about 4:30 the barrage started. We were being pounded most cruel with gas and high explosive shells but we stuck it till about 9 when your son was hit …… a piece of shell penetrated Mr. Mozley’s right breast …… I helped to bandage your son and asked him to get down to the dressing station a short distance away (it was a nasty wound and it would have got him home) but no, he refused to go, saying I will see it through Sergeant.”
“Now this splendid spirit and example inspired us all and setting our teeth we all determined to stand by to the end …… The first indication we got of the German approach was a death scream from one of the boys and after that my memory is nearly a blank for we all seemed to work by machinery, Mr. Mozley and self took up positions with revolvers and did our best, we were however surrounded by the Germans, a bomb or shell burst amongst us and I found myself with a wound in the back feeling dizzy”.
“Now as to what happened to your son I cannot say”.
Richard has no known grave and is remembered on the Pozières Memorial. This was one of his buttons:

John Roberts Coleman was the son of John Bowley Coleman and Florence Annie Coleman of 29, Derby Grove, Lenton Sands, Nottingham. His father was a schoolmaster. John was born on April 16th 1899 and he entered the High School on September 23rd 1909 at the age of ten. He was a Foundation Scholar in both 1911 and 1914. He left in July 1916 and became a Second Lieutenant in the Special Brigade of the Royal Engineers. In the era before antibiotics, he died of pneumonia in Tourcoing, after the end of hostilities, on November 26th 1918. He was only nineteen years of age, and this fresh faced young man had seen so very little of the world beyond mud, blood and death.

He is buried in Pont-Neuville Communal Cemetery in Tourcoing.
Donald James Clarkson was born on May 11th 1899. He was son of James Clarkson, whose occupation was listed as “a manager”, and his mother was called Alice. The family lived at “Wyndene”, which is now Number 52, Caledon Road, Sherwood. He entered the High School on September 23rd 1909, at the age of ten. He was always known by his many friends as “Pug” because of his upturned nose.
Donald played for the Football 1st XI as a goalkeeper during the last ever term of the sport at the High School. He was a replacement for Roy Henderson, who, by his own admission “..did horribly.., conceding eight goals… for the First Team in an away game at Trent College.” Both of them were in the Fifth Form, Year 11, at the time. In one unrecorded year, Donald was also the High School Fives champion. This is the Fives Court, which was demolished during the 1980s.
The only other specific mention of him that I have been able to find is in a rather surreal report about a meeting of the Debating Society on Saturday, February 27th 1915, when the school magazine stated that “Mr.Barber was glad Mr.Clarkson had a long arm.” Perhaps you had to be there.
Donald left in December 1915, and then seems to have gone to University College, Nottingham where he immediately joined their Officer Training Corps. After that, he went to the Royal Military Academy at Sandhurst where, in his passing out examination in early 1918, he was placed first of all the candidates in the college and was awarded the King’s Sword and the King’s Medal.
On April 23rd 1918, Donald became a Second Lieutenant in the 1/6th Battalion of the Sherwood Foresters.
Just four months later, Donald was killed in action on August 9th 1918. He is buried in Fouquières Churchyard Extension in France. This cemetery is in the village of Fouquières-les-Béthune, about one kilometre to the south-west of Béthune in the Pas-de-Calais.
Donald’s death is commemorated on the memorial of University College, Nottingham’s Officer Training Corps as well as the High School’s war memorial.
Like the two other casualties in the photograph of the OTC, he was just nineteen years of age.
I was a teacher in the High School for thirty eight years. Neither there, nor in the rest of my life, do I ever recollect knowing anybody who was called “Clarkson”. On the Commonwealth War Graves Commission website, a simple search for any casualty with the surname “Clarkson”, in the Great War, in the Army, yields 226 results.