Warren Herbert Cheale, who lived with his family in Burton Joyce, moved to the High School in January 1944 to work as an Acting Pilot Officer with the School Flight of the Air Training Corps. He was a member of the Royal Air Force Volunteer Reserve:

On Thursday, September 7th 1944, while away at camp at Wenlock in Shropshire with the boys from the High School A.T.C., poor Warren was killed in a flying accident. He was only 44 years of age. He left a widow and a teenage son and daughter. Despite his short stay at the High School, one of the boys described him as “one of the nicest people we had ever met”.
Warren, who was born in the first three months of 1900, seems to have been quite a colourful character. He lived originally at a house called Redhill in St. Helen’s Crescent. Hastings, in Sussex and the first mention of him that I can find seems to be at the age of three when, on November 28th 1903, he played the important part of Bubbles in a local production of Little Red Riding Hood:

Not very long afterwards, Warren joined up for the Great War and eventually found himself in the Royal Flying Corps.
During this era, British pilots were not allowed to wear parachutes, so Warren must have thought his death was imminent when he was involved in a mid-air collision at an altitude of over two thousand feet. The two planes must have either spun or perhaps fluttered down to earth, though, because Warren escaped with his life. That life, however, was perhaps affected by Post Traumatic Stress Disorder to some extent. It is difficult to imagine that anybody could go through an experience like that and remain completely unaffected.

On July 29th 1925, Warren married Alice Elisabeth Unwin at St. Martin-in-the-Fields Church in London.
Warren then seems to have remained in the new Royal Air Force, because the next mention seems to be in the Hastings and St Leonards Observer (Hastings, East) for June 28th 1930. Listed as a mechanic, he appeared in the local magistrates’ court, along with a young friend, who lived in the School House, North Street, Hornchurch. Both were found guilty of damaging a crop of rye in a local farmer’s field, a rather bizarre mark to leave on the pages of history, perhaps.
Certainly from 1931-1934, Warren continued to live in Hastings and St Leonards, presumably with his wife. It was a lovely place:
Warren played local cricket, both as a batsman and a bowler, although life did not always go well. For whatever reason, his wife Alice Elizabeth filed for a divorce at the London Divorce Courts in 1936. The divorce may not have gone through, because the report contains the annotation, [wd] which may well have meant “withdrawn”.
Perhaps the family then moved northwards to Nottingham as a new start, hoping to put their marital difficulties behind them for the sake of the children.
Alas, we will never know, because 21 PAFU ORB reported on that fateful September evening:
“Flying accident at Wheaton Aston. An Airspeed Oxford LX509, with Flight Lieutenant Harrison as instructor, and Pilot Officer Cheale (Air Training Corps) took off for a night flying test from Wheaton Aston and was seen to dive into the ground shortly afterwards. Both occupants were killed instantly as a result of injuries sustained.”
Here is a general map showing the location of Wheaton Aston airfield:

At the time, the Airspeed Oxford was considered to be, potentially, a rather dangerous aircraft to fly:

Although designed as a twin engined trainer, and supposedly extremely docile, it could be, in actual fact, a rather unforgiving aeroplane. Many aircraft used in RAF Training, of course, were well past their sell-by date and poorly maintained. These factors may well all have been contributory to the deaths of these two men. In actual fact, in the North Midlands, during the course of the Second World War, the majority of fatalities occurred in either Airspeed Oxfords or another old stager, the Vickers Wellington bomber. To help the situation, Oxford trainers were painted a conspicuous yellow:

The crash location on the Accident Card for this particular incident is given as:
“At Colonels Covert?, Hatton Grange, Ryton. Map Reference OS765036, just south of Hatton Grange, to the north of Ryton and just south west of RAF Cosford”.
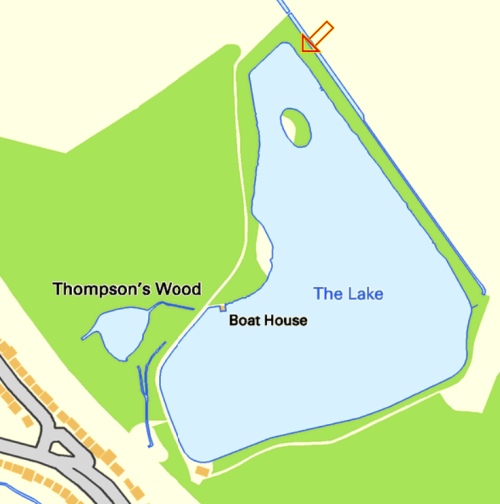
Here is a map which shows Hatton Grange:
The verdict of the official inquiry was that:
“It is not possible to form a conclusion. Investigation has not revealed the cause of the accident.”
The crew of the Oxford were:
“Flight Lieutenant Sydney Donald Harrison, aged just twenty one. He is buried in (St Ediths) Churchyard, Church Eaton, Staffordshire. He was commissioned as a Pilot Officer on February 5th 1943.
Sydney was the beloved only son of Mr and Mrs Donald Harrison, Two Trees, Hernes Road, Oxford and the grandson of Mr and Mrs T E Clarkson, The Villa, Rancliffe, near Goole.
Pilot Officer Warren Herbert Cheale (177869), RAFVR, was aged forty four. His death is commemorated at the Nottingham Crematorium. No next of kin was given at the time.”
When application for a ‘Grant of Probate’ for Warren’s will was made, his address was listed as 123 Church Drive, Burton Joyce, Nottinghamshire. This is the Main Street in that lovely village:

Interestingly, when Probate was granted on February 13th 1945, it was not to Alice Elizabeth, his presumed wife from the 1930s, but to “Rose Cheale, widow”. Perhaps that divorce had actually gone through in 1936, and this was Warren’s new wife.
Two men had paid dearly, therefore, for the High School Flight of the Air Training Corps’ week long stay in Shropshire for their annual training. They had been accompanied by at least one member of the academic staff, Mr D.C.Whimster, who was a Master at the school from 1939-1945. He was Form Master of the Fifth Form A, and may have been a teacher of English. In reminiscences published in the school magazine, the writer says, talking of drama productions:
“I wish the Society would tackle “The Knight of the Burning Pestle” again, with its greater resources and experience. Mr. D. C. Whimster’s production was interesting and creditable.”
The High School cadets were also accompanied by a person named in RAF reports as Pilot Officer Alder (Air Training Corps). This may have been somebody who normally worked at Wenlock, but I strongly suspect that this is a mis-spelling of the name of a second member of staff, namely Mr S.Allder who worked at the school from 1940-1946. As his name was “Stanley”, the boys, ever inventive, apparently called him “Stan”.
And so Warren Cheale’s extraordinary luck came to an end. In the Royal Flying Corps in 1918, he had somehow managed to avoid what must have seemed to him, as he fell earthwards for thirty seconds, perhaps a minute, a horrific and unavoidable death.
But this time, almost thirty years later, the Gods of the Air had claimed him as their own: