This blog post will introduce you to yet another killer monster (or monsters) in the long, long series of killer monsters which have ravaged different areas of France from around 1550 until the present day. I started this long list by telling you about the Beast of Gévaudan. Then it was the Beast of Benais, the Beast of Auxerre and Trucy, the Beast of Cévennes and Gard and Vivarais and then the Beast of Sarlat. This illustration has been used to represent more or less all of them by the uninhibited copyright thieves who wrote sensationalist pamphlets in the Eighteenth Century:
This time I will be looking at the area near Orléans, where a number of “incidents” have taken place over the years:
Many people at the time thought that the culprits were just ordinary wolves, but, as we will see, there are more than enough anomalies to cause the odd doubt here and there. Once again, I will be looking at a number of websites written in French, offering you my translations and you can then make your own mind up between them.
The first website actually begins with a man who was writing about wolves in the region around Orléans. Here is the coat of arms of that beautiful city:
This was in 1911, and the writer in question was an historian called Charles de Beaucorps. He wrote:
“In 1691, the wolves’ misdeeds caused many justified complaints and the Royal Commissioner duly informed the national authorities. Learning that the incidents caused by these predators were increasing every day, he asked the King to allow the inhabitants of ten or twelve parishes to have firearms in their homes. Normally they did not dare do so for fear of prosecution by the officers of the Royal Hunt. The Royal Commissioner also told them to carry out hunts and asked Monsieur Béchameil, an officer of the crown, to direct them. Nothing was done to stop this scourge: it grew to such an extent that every day people were being killed or injured by wolves. On September 12th, within musket range of the Chêne Brûlé, a parish in Cercottes, a sixty year old woman was devoured. The King’s Prosecutor in the Neuville Guard, who was keeping a register of children killed or injured by wolves using the death certificates written by parish priests, had listed more than 60 young victims in the space of fifteen months. “
Interestingly enough, this was not, apparently, completely outrageous by the usual standards of behaviour of French wolves, animals which had grown accustomed to feeding on human corpses in open charnel pits until as recently as 1820:
Charles de Beaucorps, however, was nothing if not a very thorough investigator:
“Despite the hunts and more than two hundred wolves killed, the attacks continued for years, right up until 1702 (a total of eleven years). The first teams of hunters obtained hardly any results. It needed the militia and the Duke of Vendôme, supported by thirty musketeers, to stop this scourge.
In 1700, an “Enormous Beast” was killed in the forest and brought back for the Royal Commissioner, leading to the payment of a reward of thirteen pounds.”
And nobody, of course, managed to write a precise scientific description of exactly what this “Bête énorme” was. Presumably, though, for it to be considered a “Bête énorme” in the middle of more than two hundred dead wolves, all of which must have looked pretty much the same as all the others, it cannot have been an ordinary wolf.
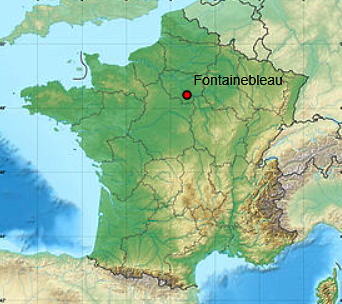
Around the same time, there were equally strange events in Fontainebleau:
“In 1679, woodcutters were killed and eaten in the Forest of Fontainebleau. The parish registers of Bois-le-Roi mentioned several cases of attacks.”
It might have been wolves, but I am surprised that, if it were, they did not say so. As the map shows, these gory killings took place not a million miles from Orléans:
Shortly after this, came the animal which was to become really famous. It was given the name of “The Beast of Orléans”. According to a website we have already visited:
“There were actually two distinct episodes which took place almost a century apart. The first, the Beast of Orléans, happened in 1709, as attested by a letter from Monsieur Polluche Lumina, who lived in the Rue des Hennequins, dated June 17th 1765. It says this:
“I am taking the liberty to write to you about the ferocious Beast of Gévaudan. The more I reflect on all the stories which appeared in the newspapers the more I find a resemblance with what has happened here and what I myself saw in part after the Great Winter of 1709. There appeared an animal which people called “The Beast” which only attacked women and children. There were the same ways of moving around, the same
sharpness and even timidity as the Beast of Gévaudan:The devastation was so serious that in six months there were more than 100 people killed and as many wounded. This provoked the king to send his royal wolf catchers. The officer who commanded them did not bother to follow the trail of destruction which this animal produced and which was normally around the perimeter of the forest.
He decided instead, every morning, to have several hunts in the woods with bloodhounds, after which his men went on a reconnaissance. Then, without making any noise whatsoever, they positioned marksmen all around the area. The dogs were then released into the forest.
If the Beast was not found, they would go and carry out the same tactics in another area to pursue the Beast. There was hardly any hunt where the men did not kill one, two or three wolves, because the Beast was nothing different from them. Could they not employ the same tactics to destroy the so-called Beast of Gévaudan? I presume that the situation there is just like it was here. Just wolves and nothing more. I forgot to say that they killed a good hundred wolves in this area. In the stomach of several they found hair and other things which proved that they had eaten human flesh. They managed to destroy the species, the wolf, to such a point that there was no longer any question of there being a so-called “Beast” to which fear had given names and features each one more frightening than the last.”
Clearly, Monsieur Polluche Lumina thought that the Beast of Orleans was merely a wolf or wolves, seen under conditions of extreme stress and fear. Such terror supposedly exaggerated the witnesses’ testimony to such an extent that the idea of a monster was born. Not everybody, though, went for this rather simplistic explanation.
A short pamphlet about the Beast was printed at Chartres by Garnier-Allabre, the well-known local manufacturer of wallpaper and pictures. He may well have interviewed the witnesses about what they had seen. Garnier-Allabre produced this illustration which, to me, looks nothing like any wolf I have ever seen, even a stylised one. It has scales! It is armoured! It is as much like an anklylosaurus as a wolf!:
The leaflet also contained the following text:
“This cruel beast tears and devours everything it encounters in its path and causes desolation among whole families in the areas that it moves through. Last December 25th, near the entrance to a village near Beaugency, it found an unfortunate woodcutter and his wife and his eldest son. The ferocious beast first attacked the unfortunate woman. The poor woodcutter and then his son tried to defend her and a terrific battle ensued. Despite their efforts and those of several other people who rushed to the rescue, the unfortunate woman was killed and several others were wounded.
It is impossible to calculate the number of unfortunate people who were victims of the rapacity of this wild beast; it is covered with scales, and no weapon has any effect on it. Let us pray to God, my dear friends, to deliver us from this monster, and pray, too, for the speedy recovery of those injured by this animal. “
The local historian Monsieur Lottin also makes mention of the Beast and links the Beast of Orléans to the Beast of Gévaudan:
“A cruel beast, believed to be a hyena and which ravaged Gévaudan, Auvergne, Nivernais , Bourbonnais and the areas around Orléans and against which regular frontline troops had operated , was killed at that time , by the Sieur Antoine, a skilful hunter. This ferocious animal had caused the greatest devastation and had inspired universal terror. Coloured pictures, produced by Monsieur Letourny, a paper merchant in the Place du Martroi , who had gained a reputation for this kind of engraving, were sold by the thousand.”
Alas, none seem to have survived.
Extremely close to Orléans is the tiny town of Chaingy. It is represented by the red square:
Even nowadays Chaingy has only 3,669 inhabitants. It was here that an unbelievably aggressive creature struck more than a century after “The Beast of Orléans”. The same website continues:
“In 1814, the Beast of Chaingy also gave rise to an abundance of images. There has been much confusion between the two creatures, at least on the level of how the illustrations would represent “The Beast”. This is not surprising: the printers did not trouble themselves over exact details and were more than willing to copy each other’s efforts:
The case of the Beast of Chaingy took place in 1814. It is possible that it reflected other cases of “Beasts” from a long time before, such as the one described by Monsieur Polluche Lumina which took place a long time before (1709). The Beast of Chaingy is a creature which has been a little better documented :
“On December 6th, 1814 , several women and children who were collecting dead wood in the forest were attacked by a she-wolf . The animal killed two and injured eight more. The Baron de Talleyrand, whose magnificent full name was Alexandre Daniel de Talleyrand-Périgord was Prefect of this area. He ordered a hunt and the beast was slain near Cercottes.”
This is as maybe, but, for me, if this creature was just an ordinary canis lupus, then its behaviour was absolutely extraordinary. Nobody nowadays would expect a group of people to be attacked, or even challenged, in a wood by a lone she-wolf. To then have two individuals killed and eight more wounded is quite astonishing. All I can suggest is that this animal was, as has been said so many times both about the Beast of Gévaudan and about many others:
“C’était comme un loup mais ce n’était pas un loup.”
“It was like a wolf but it was not a wolf.”
In 1868, the last real wolf in the region was killed by a poacher in Chaingy, a man called Blaise Basset. The body of the animal is now on display at the Museum of Natural Sciences in Orléans.
And here it is:
Hardly the type of creature to kill two people and wound a further eight. I’m more scared of those polyester slacks if truth be told.
And finally. Let’s hope that this is merely an imaginative drawing of the Beast of Chaingy. If it’s from a trailcam, we could all be in trouble: